北京交通大学光波技术研究所全光网络与现代通信网教育部重点实验室,北京 100044
提出了一种基于亚波长偏振保持光纤的多维复用与折射率(RI)传感集成器件。该器件由定向耦合器、Y型分束器和布拉格光栅器件构成,能够同时实现三维空间中偏振和频率(解)复用、色散补偿以及RI传感功能。集成器件下行端口输出偏振解复用后的x偏振态,其在0.25 THz频率处的传输率和消光比分别为-5.94 dB和15.16 dB。此后,原波导中y偏振态(工作频率为0.25 THz)与x偏振态(工作频率为0.27 THz)复用后于直通端口输出,传输率分别为-7.20 dB和-2.02 dB。同时,集成的均匀光栅和π相移光栅可分别实现色散补偿(群速度色散为-109.4 ps·THz-1·mm-1)和RI传感(灵敏度为0.181 THz/RIU)功能。基于太赫兹亚波长光纤的集成器件在下一代通感一体化信息系统中具有良好的应用前景。
光学器件 太赫兹 耦合器 复用器 传感器
北京交通大学光波技术研究所全光网络与现代通信网教育部重点实验室,北京 100044
提出了一种空气孔辅助型偏振保持少模光纤,在椭圆环芯中心引入一个椭圆形空气孔,并在水平和竖直方向分别引入4个不同尺寸的圆形空气孔,以提高模式间的有效折射率差,实现多阶模式间无串扰偏振保持传输。通过数值仿真研究了4个圆形空气孔的尺寸和位置、环形纤芯的尺寸和椭圆率以及椭圆形空气孔的尺寸和椭圆率对偏振保持传输性能的影响。经过参数优化设计,所提光纤在1520~1600 nm波段内满足所有相邻模式间的有效折射率差Δneff均高于1.0×10-4,色散为17.6~51.3 ps/(nm·km)。所提光纤在大容量空分复用通信技术中具有良好的应用前景。
光纤光学 偏振保持 空气孔辅助 空分复用 少模光纤 中国激光
2022, 49(17): 1706001
北京交通大学光波技术研究所全光网络与现代通信网教育部重点实验室,北京 100044
现代光网络需要满足高速、大带宽,大容量传输技术。基于反谐振反射光波导机制,提出一种偏振保持(PM)空芯光纤。光被正交方向上厚度不同的4个套管限制在空气芯子中来实现有效的PM传输。为了实现提高PM性能的同时降低传输损耗,研究了套管中反谐振层的数量、套管厚度、空气芯子尺寸以及正交方向上相邻两个套管之间距离的影响。数值仿真结果表明,所提出的反谐振空芯光纤在1550 nm处支持两种正交偏振模式,HE11x和HE11y模式的双折射为1.2×10-4,传输损耗分别为0.002 dB/m和0.013 dB/m。此外,在1425~1725 nm(带宽为300 nm)内,光纤的双折射不低于1.0×10-4,传输损耗在0.002 dB/m~0.185 dB/m范围内,色散值低于45.51 ps?nm-1?km-1)。同时,由于采用空芯结构的设计,光纤具有较低的弯曲损耗。所提出的光纤在需要短距离,大容量和低时延传输的数据中心和金融网络系统等领域具有较好的应用前景。
双折射 反谐振反射光波导 偏振保持 空芯光纤 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(23): 2326001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of All Optical Network & Advanced Telecommunication of EMC, Institute of Lightwave Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
2 Zhengzhou Xinda Institute of Advanced Technology, Zhengzhou 450001, China
3 Department of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineering, Osaka Institute of Technology, 5-16-1 Omiya, Asahi-ku, Osaka, 535-8585, Japan
4 Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology, Okayama University, 1-1-1 Tsushimanaka, Kita Ward, Okayama Prefecture, 700-8530, Japan
Metamaterial absorbers (MAs) serve as important electromagnetic wave-absorbing devices that have captured the attention of researchers for a long term. Functioning as sensitive detectors to determine perturbations in an ambient environment is another significant subsidiary function. Here, we theoretically propose an optimized fabrication method to implement terahertz MAs with fewer steps and also evaluate both absorption and sensing performances of such MAs realized by the new method. Simulation findings demonstrate that such MAs can basically maintain the original absorption features perfectly, including near-complete absorption at resonance as well as strong robustness to wide incident angles. Specifically, the full width at half-maximum and quality factor of the absorption resonances attenuate less than 26% and 8% with this new method, remaining in the ranges of and for two selected example MAs. More significantly, sensing capacities of this type of MA, in terms of maximum detection range (enhancing at least 9%), observable spectral modulation (increasing at least 6.3%), and refractive index sensitivity, are improved to a large extent because of more intense coupling between resonant field and matter in the case of surface-relief MAs. This stronger coupling results from exposing more spots of the resonantly high field to direct contact with an approaching analyte, which is illustrated by field profiles of the MAs at resonance in this work. Additionally, other desirable absorber features are also explored with such MAs, like functioning as building blocks to configure multiband MAs and strong robustness against fabrication errors. Such new-style terahertz MAs shown in the paper, acting as good examples, not only prove that terahertz MAs can be fabricated by the proposed time- and cost-saving route in contrast to the traditional MA fabrication process, but also can serve as novel platforms to explore other intriguing terahertz photonic effects, such as the field enhancement effect.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(4): 04000519
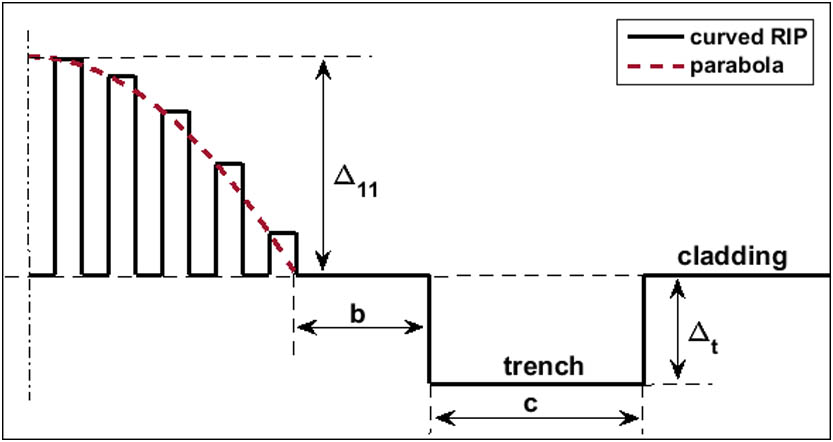
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Lab of All Optical Network & Advanced Telecommunication Network of EMC, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
2 Institute of Lightwave Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
We present a single-mode multilayer-core fiber with a large mode area (LMA) and a low bending loss in this Letter. A low equivalent core-cladding refractive index difference is achieved by exploiting the multilayer structure. The multilayer structure has a better bending performance than a traditional step-index core and this structure also contributes to realizing different curved refractive index profiles that have a better bending performance. An index trench is also introduced to dramatically reduce the bending loss. The experimental results show that, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, the mode area of the fabricated fiber is about 215.5 μm2 and the bending loss is 0.58 dB/turn at a 10 mm bending radius. The LMA and excellent bending performance can be obtained simultaneously with the proposed fiber.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2310 Fiber optics 060.2400 Fiber properties 060.2430 Fibers, single-mode Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 120601





